How To Figure Out Number Of Register Cpu
Different Classes of CPU Registers
In Computer Architecture, the Registers are very fast reckoner retentivity which are used to execute programs and operations efficiently. This does by giving access to commonly used values, i.east., the values which are in the point of operation/execution at that time. So, for this purpose, there are several unlike classes of CPU registers which works in coordination with the estimator memory to run operations efficiently.
The sole purpose of having annals is fast retrieval of data for processing by CPU. Though accessing instructions from RAM is comparatively faster with hard bulldoze, information technology still isn't enough for CPU. For fifty-fifty better processing, there are memories in CPU which can become data from RAM which are about to exist executed beforehand. After registers we accept cache retentivity, which are faster merely less faster than registers.
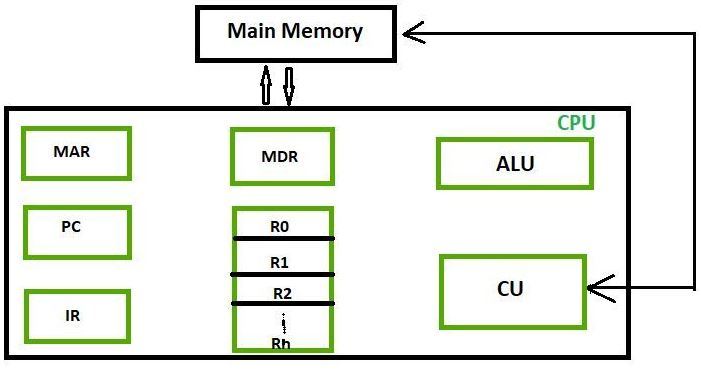
These are classified as given beneath.
- Accumulator:
This is the most frequently used register used to store data taken from memory. It is in different numbers in different microprocessors. - Retentivity Accost Registers (MAR):
It holds the address of the location to be accessed from retentiveness. MAR and MDR (Retention Data Register) together facilitate the communication of the CPU and the main memory. - Memory Data Registers (MDR):
It contains data to be written into or to be read out from the addressed location. - General Purpose Registers:
These are numbered as R0, R1, R2….Rn-one, and used to store temporary data during whatsoever ongoing operation. Its content tin can be accessed by assembly programming. Modern CPU architectures tends to apply more GPR so that register-to-annals addressing tin be used more than, which is comparatively faster than other addressing modes. - Programme Counter (PC):
Program Counter (PC) is used to proceed the runway of execution of the program. It contains the memory address of the next pedagogy to be fetched. PC points to the accost of the adjacent instruction to exist fetched from the primary retentiveness when the previous instruction has been successfully completed. Programme Counter (PC) also functions to count the number of instructions. The incrementation of PC depends on the type of architecture existence used. If nosotros are using 32-flake architecture, the PC gets incremented past 4 every time to fetch the next instruction. - Instruction Annals (IR):
The IR holds the pedagogy which is merely near to be executed. The instruction from PC is fetched and stored in IR. Equally shortly as the instruction in placed in IR, the CPU starts executing the educational activity and the PC points to the next education to exist executed. - Condition code register ( CCR ) :
Condition lawmaking registers comprise different flags that signal the status of any operation.for instance lets suppose an operation acquired creation of a negative result or zero, so these flags are set high accordingly.and the flags are
- Carry C: Set to 1 if an add operation produces a behave or a decrease performance produces a borrow; otherwise cleared to 0.
- Overflow V: Useful but during operations on signed integers.
- Nothing Z: Set to 1 if the outcome is 0, otherwise cleared to 0.
- Negate N: Meaningful only in signed number operations. Prepare to 1 if a negative result is produced.
- Extend X: Functions as a carry for multiple precision arithmetics operations.
These are generally decided by ALU.
And so, these are the different registers which are operating for a specific purpose.
How To Figure Out Number Of Register Cpu,
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/different-classes-of-cpu-registers/
Posted by: sharponowen.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Figure Out Number Of Register Cpu"
Post a Comment